
Luckily, the cybersecurity and international threats posed by the anonymity of the dark web are continuously being thwarted by government bodies, law enforcement agencies, and thousands of information technology professionals. Help Address Today's Biggest Cybersecurity Challenges The dark web's anonymity has also led to cybersecurity threats and various data breaches over the last few decades. Several sites hosting illegal material have been discovered by government agencies and shut down in recent years, including Silk Road, AlphaBay, and Hansa.
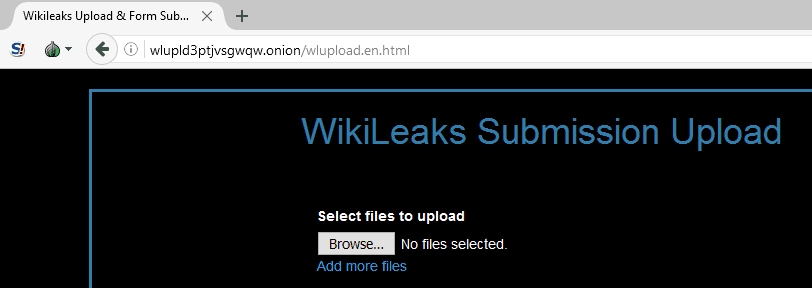
These include the buying and selling of illegal drugs, weapons, passwords, and stolen identities, as well as the trading of illegal pornography and other potentially harmful materials. Given its anonymous nature, the dark web is also used for illicit and even illegal purposes. Despite these added layers of security, users should still be cautious using the dark web and take proper security measures, such as periodically updating their security software, browsing with a robust VPN, and avoiding the use of a standard email address. For example, in countries where government surveillance may be used to spy on and oppress political dissidents, the dark web is often a place for communication that avoids government censorship and scrutiny. While using the dark web may seem suspect on the surface, it is perfectly legal, and there are many legitimate uses of Tor and anonymous browsing. When users access a site through Tor, their information is routed through thousands of relay points that cover the user's tracks and make their browsing virtually impossible to trace. It uses a technology called "onion routing," which protects users from surveillance and tracking through a random path of encrypted servers. People use the dark web for both legal and illegal purposes. Originally used by the United States Department of Defense to communicate anonymously, the dark web has now become a hub for users wishing to remain anonymous around the world. With the creation of Tor, users could now browse the internet completely anonymously and explore sites that were deemed part of the "dark web." How the Dark Web Works That groundwork was the basis for the Tor Project, which was released in 2002 and launched a browser in 2008. The dark web is known to have begun in 2000 with the release of Freenet, the thesis project of University of Edinburgh student Ian Clarke, who set out to create a "Distributed Decentralised Information Storage and Retrieval System." Clarke aimed to create a new way to anonymously communicate and share files online. In general, most average internet users will never need to access content on the dark web, although it is perfectly legal to use Tor. What's known as the dark web exists within the deep web it's an area of the internet that is only accessible by users who have a Tor browser installed. These pages are not indexed by search engines and are protected behind security walls, authentication forms, and passwords on the deep web.Īpproximately 90% of all websites are on the deep web, and many are used by entities such as corporations, government agencies, and nonprofits. Millions of regular internet users access private databases such as email inboxes and credit card accounts daily. What's the Difference Between the Deep Web and the Dark Web? In a classic example, the surface web can be imagined as the tip of a large iceberg whose bulk remains hidden just under the surface.

org sites, it's estimated that it represents only around 5% of the total content available on the internet, with the rest being found on the deep web or dark web.
Although the surface web is made up of many of the most popular. Sites on the surface web are also indexable and can be easily found using search engines. Sites on the surface web (or open web) are those visible to average users without the use of Tor or any other special browsers or software. Information Technology Program Master in Cybersecurity Management Cyber Defense Graduate Certificate What Is the Surface Web?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
